Key in a search term below to search our website.
Key in a search term below to search our website.
Robots come in many different shapes and sizes, from factory tools to human-looking androids and toys. Find out about Freddy the robot, developed in the 1970s at the University of Edinburgh, and explore how robot technology has changed from early automota to assisting surgery and exploring Mars.
“I can’t define a robot, but I know one when I see one.- Joseph Engelberger, Engineer and pioneer of industrial robots
Date
c.1970
Made from
Metal, plastic
Museum reference
On display
Explore, Level 1 of the Science and Technology galleries at the National Museum Of Scotland.
Did you know?
Freddy the robot was the world’s first thinking robot to combine a seeing eye and feeling hand.
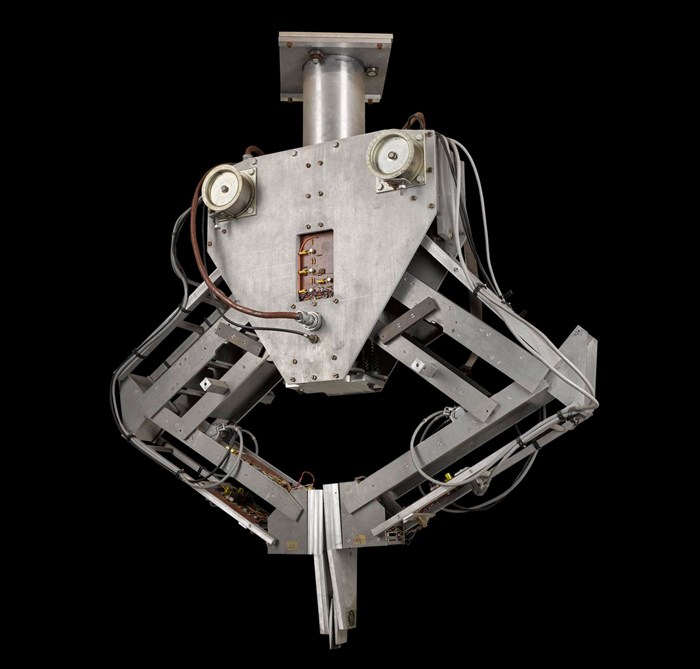
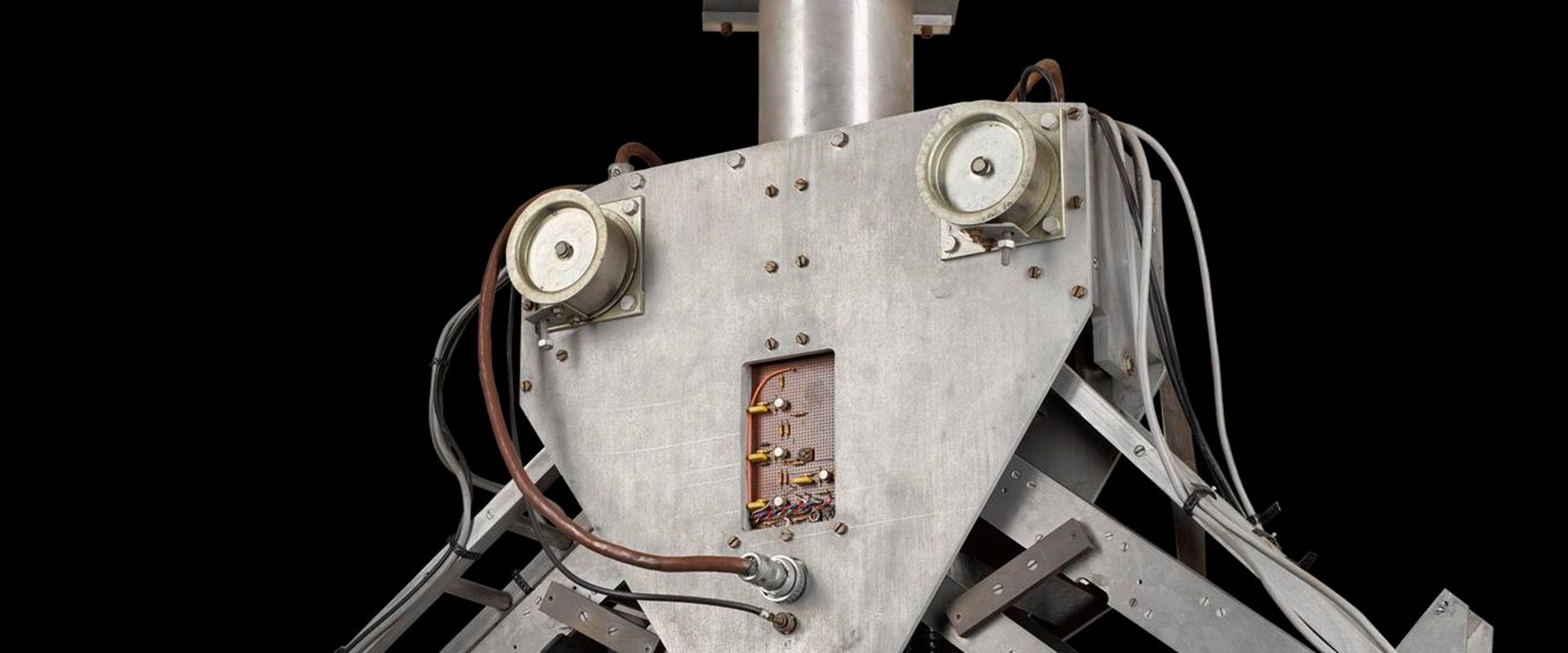
Freddy was built in the early 1970s, by researchers at the Department of Artificial Intelligence (AI), University of Edinburgh.
Freddy the robot was the world’s first thinking robot to combine a seeing eye and feeling hand.
There were two ‘Freddys’ - the Museum’s robot here is Freddy II. Freddy I was made between 1969 and 1971.
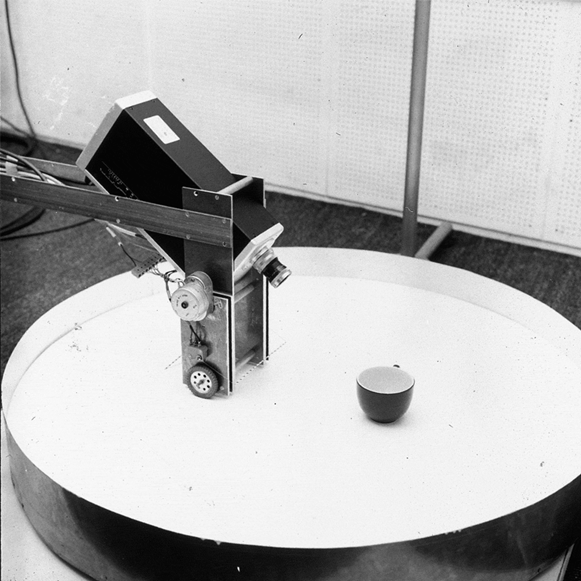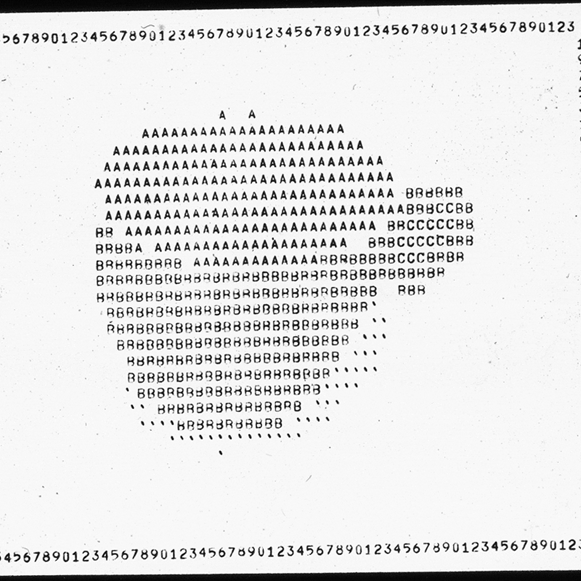
Freddy I identifying a cup. Image © University of Edinburgh
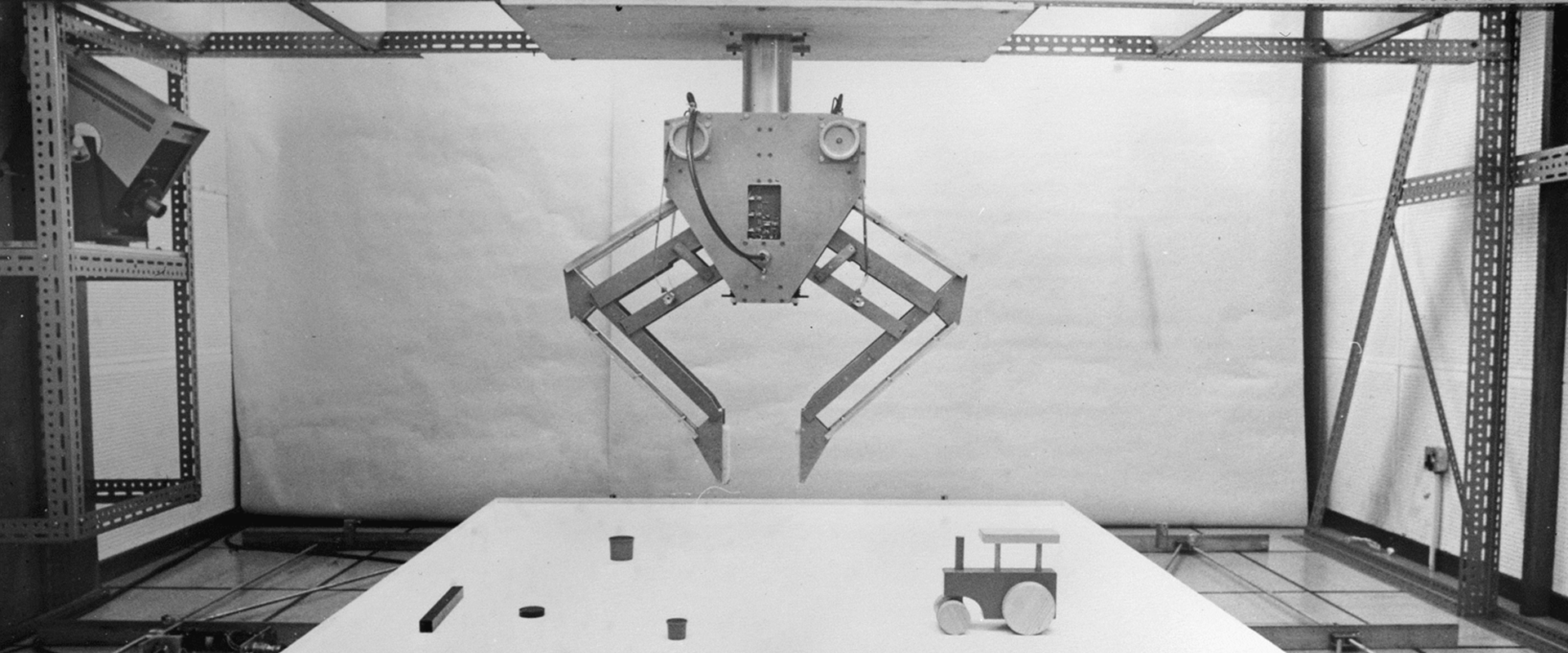
Freddy was run by two computers, programmed with the moves that the robot might have to make, and with scenarios that it might encounter.
These computers were linked up to two camera ‘eyes’, one looking straight down and one at an angle and its grip was pressure sensitive. The platform beneath the robot’s hand moved side to side and back and forwards.
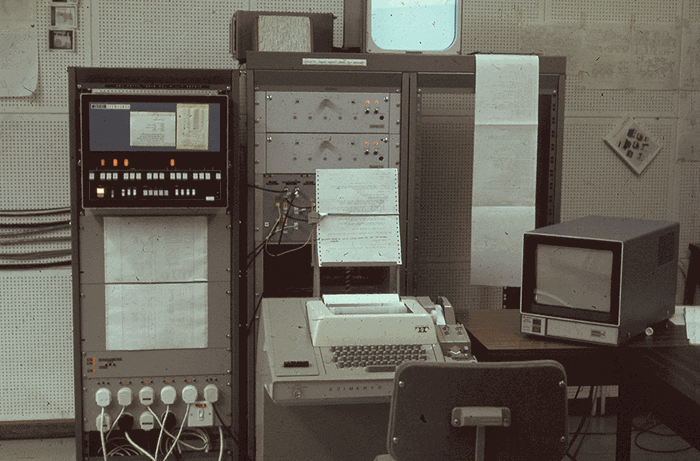
The smaller of Freddy’s two computers. Image © University of Edinburgh
Freddy was designed to perform a few tasks in a similar way to a five-year-old child. But the development team found they had underestimated how intelligent a five-year-old child could be.
One task that they taught Freddy was to put scattered pieces into a box, but the robot did the job too well and tried to tidy the box away too.
One of Freddy's challenges. Image © University of Edinburgh
This film shows the robot assembling a toy car and boat from a pile of parts. The task took about 16 hours – so we’ve speeded up the film!
Automata are machines which work by themselves, usually with a clockwork mechanism. Music boxes are a simple example. Since the 18th century, automata have been made which can write, draw or play musical instruments. Automata mechanisms were also used to move stuffed birds animals.
The word robot was first used in 1920, in a play by Czech playwright Karel Čapek Rossum’s Universal Robots (Rossumovi Univerzální Roboti).
Čapek’s play was about a factory which made artificial workers. Many works of fiction have explored what robots might become, and what they might mean for society.
In 1961, the world’s first industrial robot began work at a car factory. Called UNIMATE, it was designed in 1956 by American inventors George Devol and Joseph Engelberger. They were inspired by science fiction to create a working robot which could carry out tasks which were unpleasant for people, such as moving hot pieces of metal and welding.
Designed and built at the Stanford Research Institute in the USA, between 1966 to 1972, Shakey was the first mobile robot which used artificial intelligence to move, without direct instructions from people. Shakey used a TV camera and ‘bump sensors’ to stop it knocking into things. The robot moved at only two metres per hour.
Today many robots are designed to carry out tasks in dangerous environments, exploring in space, or deep under the ocean. Curiosity is a robot explorer on Mars and will never return to Earth. Mainly controlled by radio signals from Earth, Curiosity was also designed to choose its own route to a given destination.
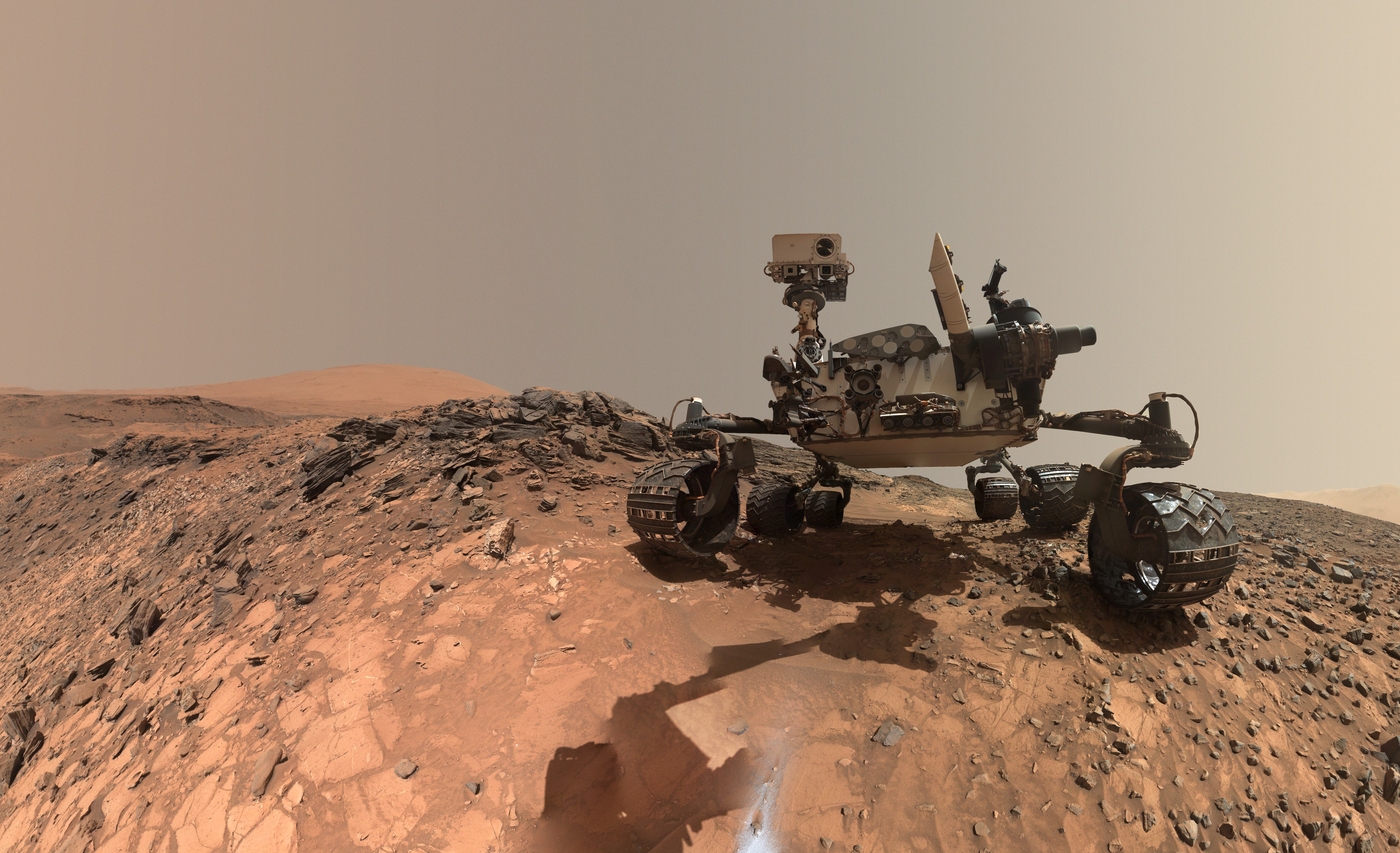

Mars Curiosity, self-portrait 2015 © NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS

'Dispensing robot in pharmacy' by Adrian Wressell. Credit: Adrian Wressell, Heart of England NHS FT. CC BY
The German robotics company, Festo, have built many pioneering robots based on studies of the natural world. These fly, swim, hop or scurry like the insects, animals and birds they are based on, providing inspiration and solutions for future technologies.
In 1985 a robot was used in surgery for the first time, to place a needle precisely in a brain. Robot surgeons can help surgeons operate with smaller, precise movements, without hand tremors, and through small incisions. They can be used together with medical scans
In this film, the da Vinci Surgical System is used to stitch the skin back onto a grape.
NASA uses robots in many different ways. Robotic arms can move large objects in space, and robotic spacecraft can visit other worlds. This film shows how an automated observatory like Spitzer, which is effectively an astronomy robot, spends its time.