Key in a search term below to search our website.
Key in a search term below to search our website.
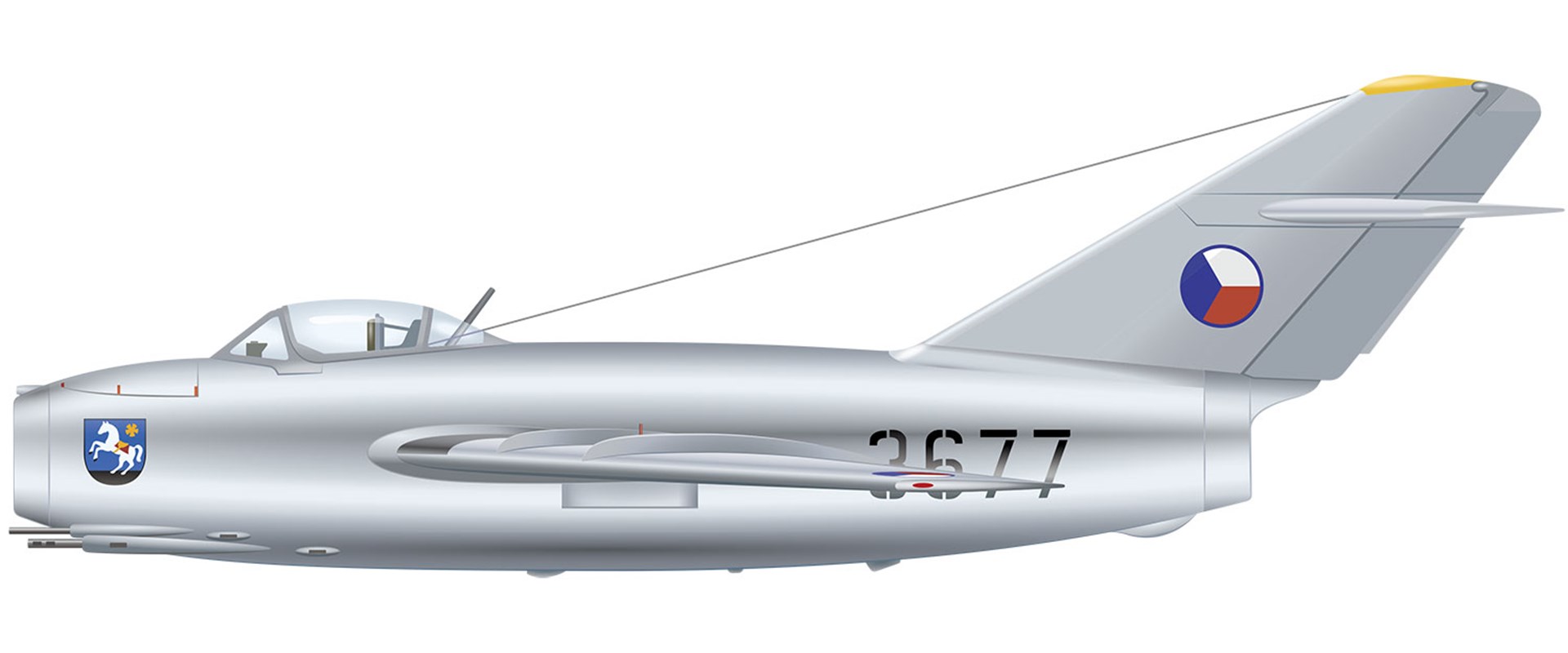
Between 1954 and 1958, Czechoslovakia (now the Czech and Slovak Republics) used the S-103 as its main jet fighter.
The S-103 was superior to western jet fighters of the time. In 1953, a US Air Force jet was shot down after it strayed into Czechoslovakian airspace.
This example was flown by the Czechoslovakian 11th Air Regiment. The crest of the city of Ostrava is painted on the nose.
| Date: | 1956 |
| Crew: | 1 (pilot) |
| Top speed: | 658 mph (1,059 km/h) |
| Range: | 771 miles (1,240 km) |
| Weapons: | 2 x 23 mm cannon 1 x 37 mm cannon 2 x 100 kg of bombs or rockets |
Find out more about the design of the Aero S-103 in this short animation, from 40 seconds viewing time.
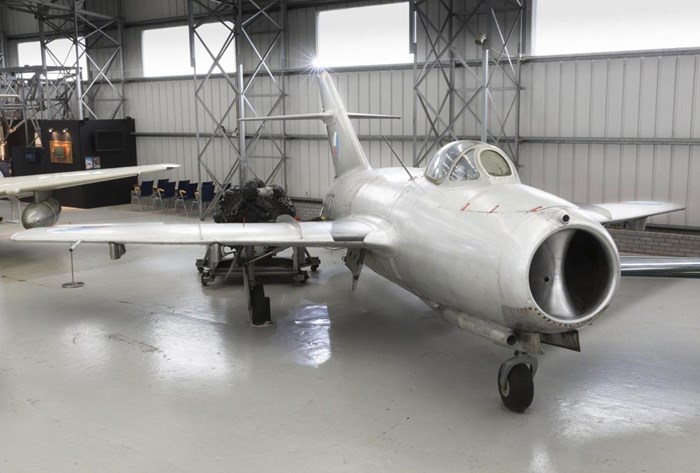

The Aero S103 in the Military Aviation hangar at National Museum of Flight.

Close-up of white horse image on the Aero S-103 at National Museum of Flight.
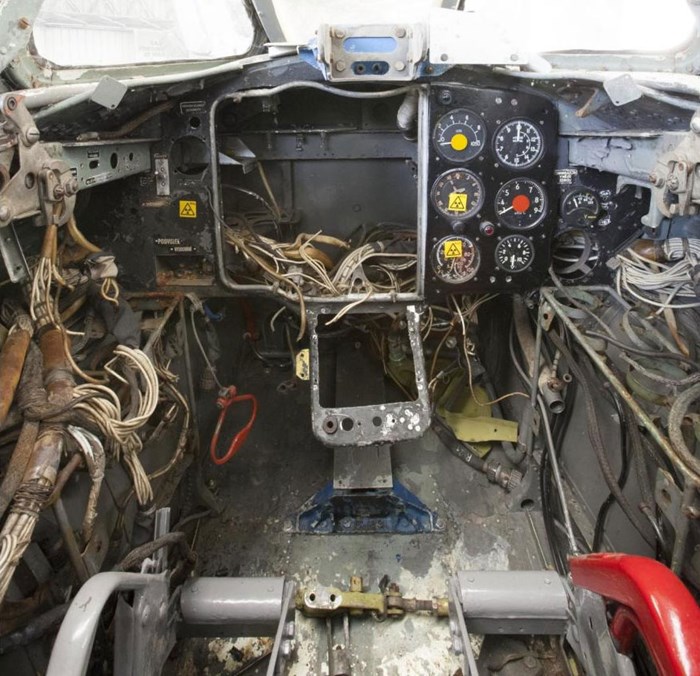

The cockpit of the Aero S-103.
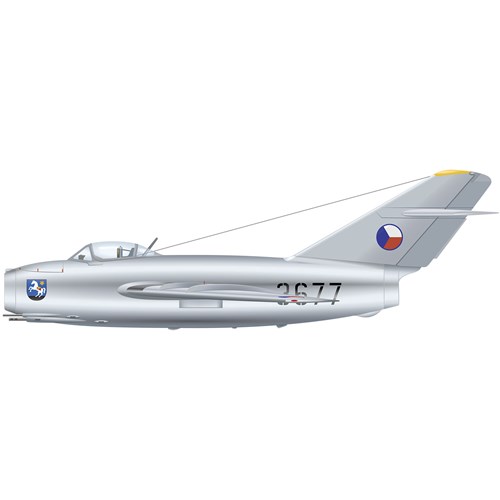

Between 1954 and 1958, Czechoslovakia (now the Czech and Slovak Republics) used the S-103 as its main jet fighter.
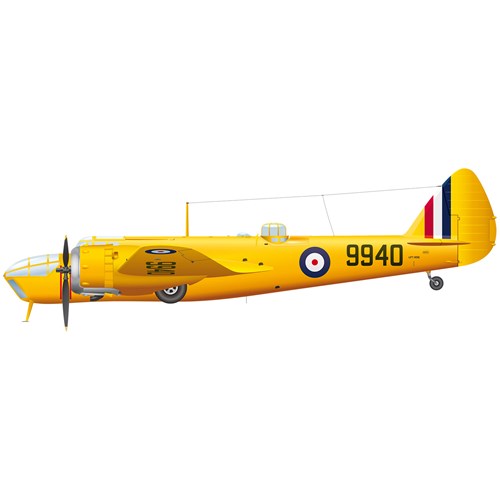

The Bolingbroke was the name given to the Bristol Blenheim light bomber built under licence in Canada.
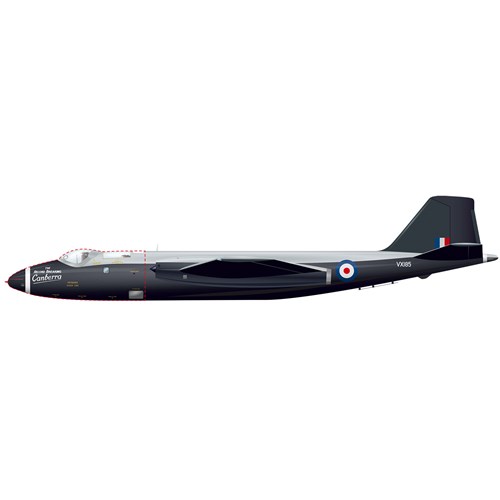

The Canberra was the first Royal Air Force bomber powered by jet engines.
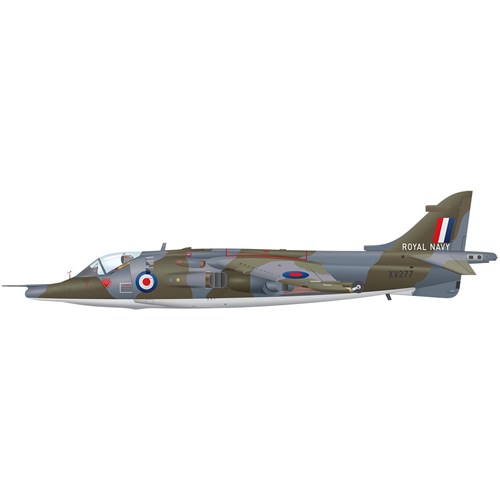

Known as the ‘jump jet’, the Harrier was the world’s first vertical take-off combat aircraft to enter operational service.
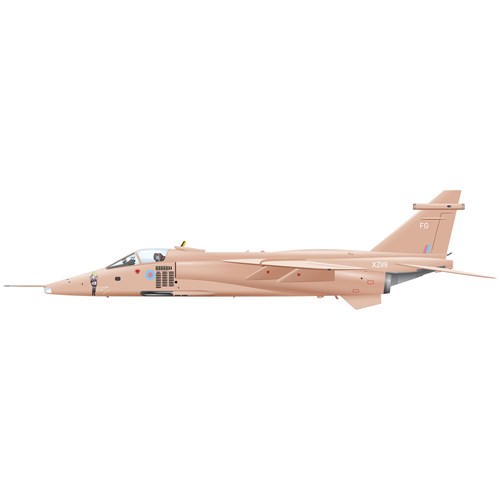

The Jaguar was a tactical strike and reconnaissance fighter which could carry nuclear weapons.
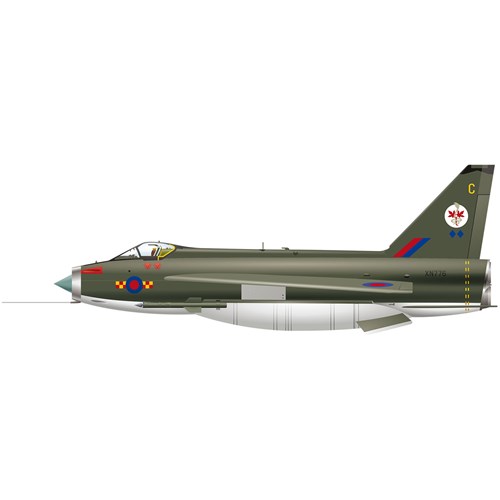

The Lightning was the first supersonic jet fighter in the Royal Air Force.
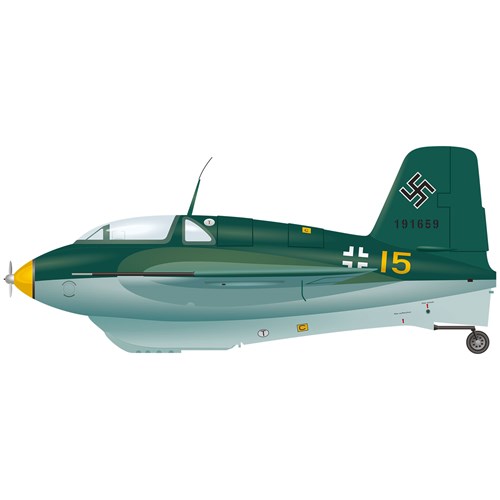

The rocket-powered Komet was the fastest aircraft of the Second World War.

The Meteor was the Royal Air Force’s first jet fighter. It entered service in 1944.
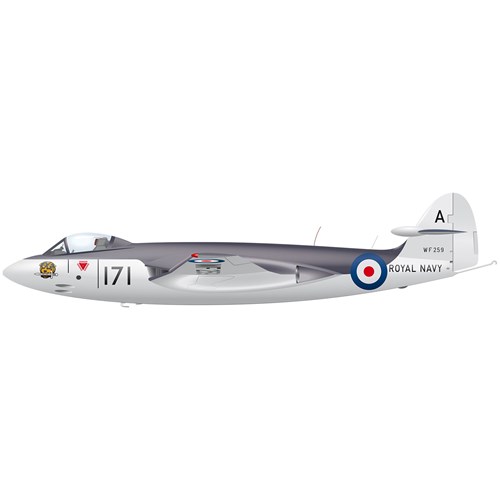

The Sea Hawk was a single-seat jet fighter which entered service with the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm in 1953.
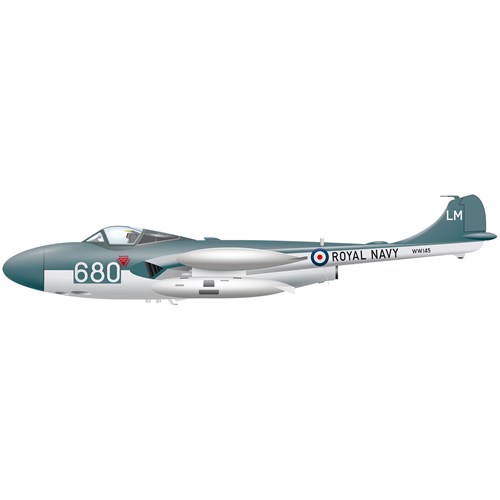

The Sea Venom was the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm’s first all-weather jet fighter.
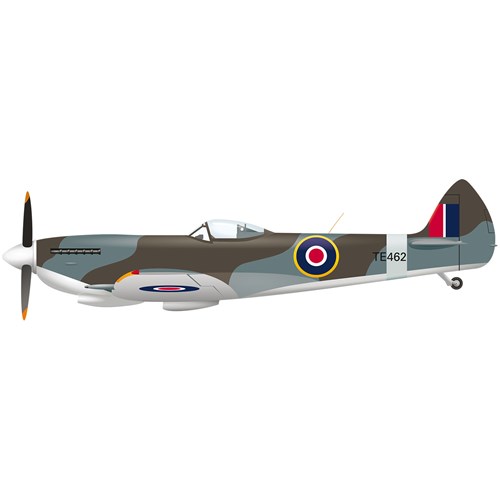

The Spitfire is the most famous of all British combat aircraft.
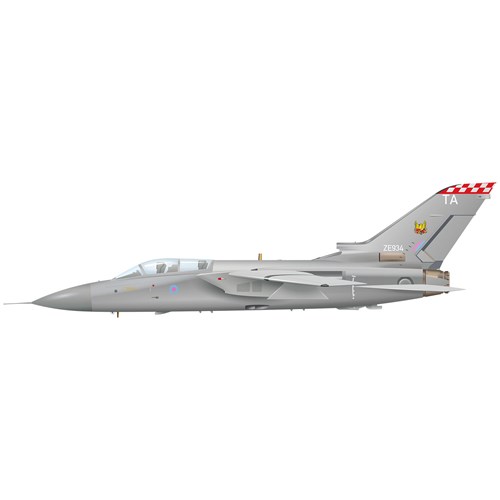

The Tornado was the Royal Air Force’s only variable geometry (swing wing) aircraft.